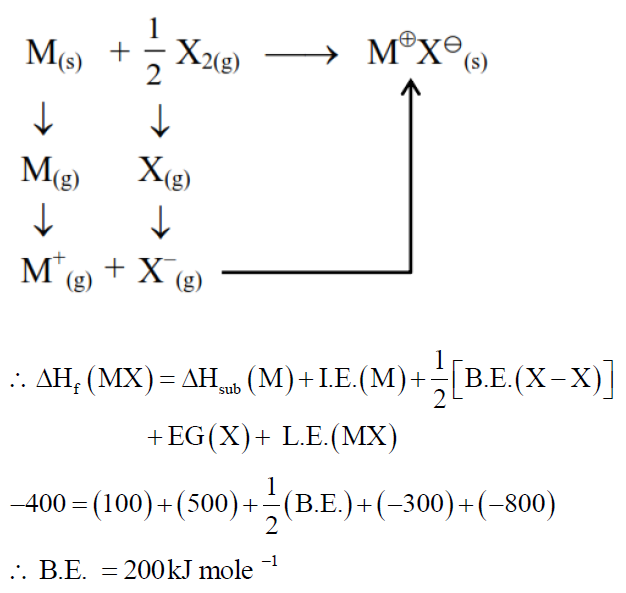
The bond dissociation enthalpy of $\mathrm{X}_{2} \Delta \mathrm{H}_{\text {bond }}^{\circ}$ calculated from the given data is $\_\_\_\_$ $\mathrm{kJmol}{ }^{-1}$. (Nearest integer)
$\begin{aligned} & \mathrm{M}^{+} \mathrm{X}^{-}(\mathrm{s}) \rightarrow \mathrm{M}^{+}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{X}^{-}(\mathrm{g}) \Delta \mathrm{H}_{\text {lattice }}^{\circ}=800 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} \\ & \mathrm{M}(\mathrm{s}) \rightarrow \mathrm{M}(\mathrm{g}) \Delta \mathrm{H}_{\mathrm{sub}}^{\circ}=100 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} \\ & \mathrm{M}(\mathrm{g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{M}^{+}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{e}^{-}(\mathrm{g}) \Delta \mathrm{H}_{\mathrm{i}}^{\circ}=500 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} \\ & \mathrm{X}(\mathrm{g})+\mathrm{e}^{-}(\mathrm{g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{X}^{-}(\mathrm{g}) \Delta \mathrm{H}_{\mathrm{eg}}^{\circ}=-300 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} \\ & \mathrm{M}(\mathrm{s})+\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{X}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow \mathrm{M}^{+} \mathrm{X}^{-}(\mathrm{s}) \Delta \mathrm{H}_f^{\circ}=-400 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}\end{aligned}$
[Given : $\mathrm{M}^{+} \mathrm{X}^{-}$is a pure ionic compound and X forms a diatomic molecule $\mathrm{X}_{2}$ in gaseous state]